Modern software development is in a phase of constant change, rapid innovation, and increasing customer expectations. Every development cycle, whether it is a small enterprise SaaS or a mobile app, requires clarity, project planning in software project management coordination and control right from the start. Project planning is no longer a phase in the software project management process. It has become a critical strategic function which determines success or failure.
Software projects used to follow a simple process. The requirements were collected, the team of developers wrote the code and then the final product would be delivered several months or even years later. Today's world is totally different. The requirements are constantly changing, technology is improving rapidly and the product expectations are shifting at a rapid pace. In this dynamic environment, project managers need to move beyond traditional planning, adopting a future-ready strategy that embraces modernization, flexibility, and intelligent decision making.
This blog explores how to plan a software project, from start to finish. This blog explains the planning phase, what it is, what elements are required, how teams can prepare for challenges and how to make planning future-ready.
Software development is more dynamic than it was a decade back. In the past, teams would work on linear, simple projects that had clear instructions. Software products today include:
Due to this complexity, project planning in software project management traditional planning is no longer effective. Success of a project depends now on how well the team plans ahead before execution begins.
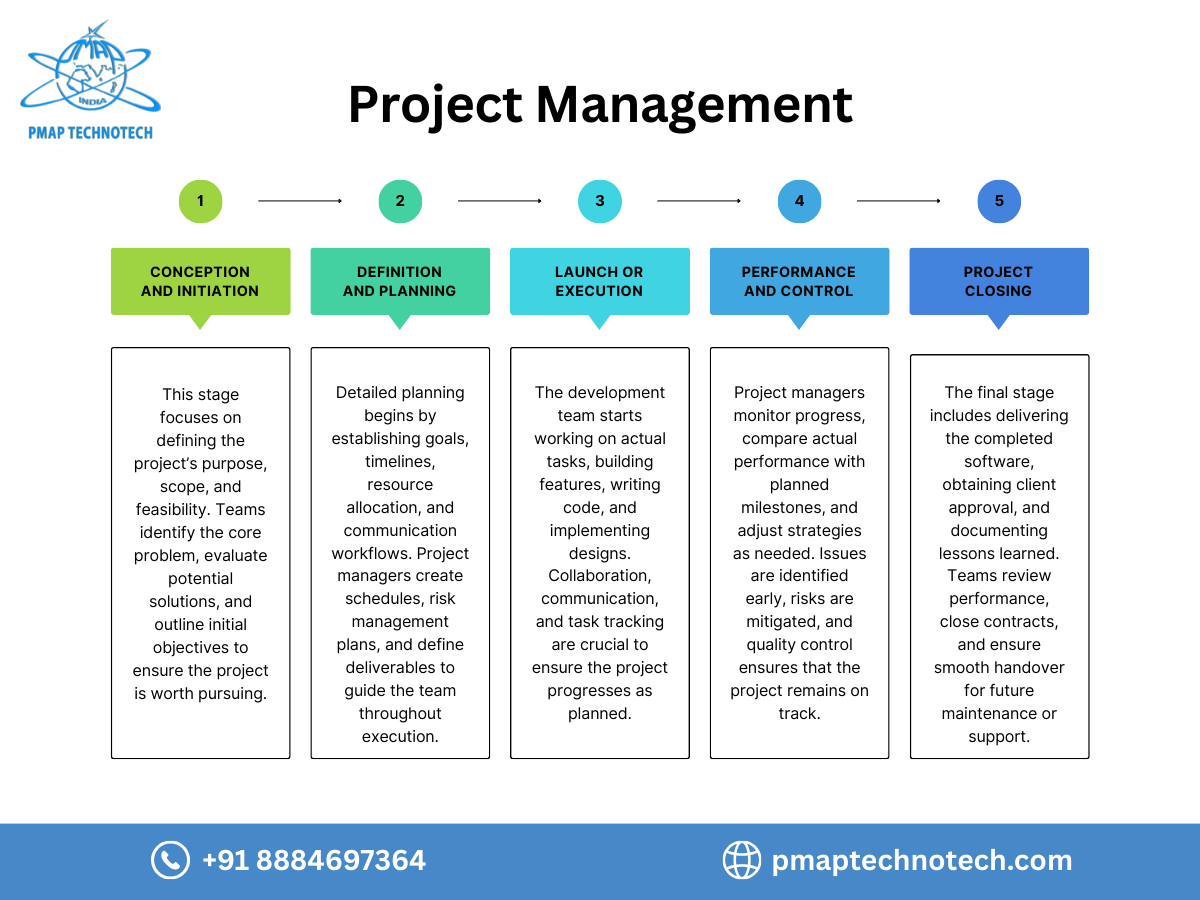
Project planning is fundamental to software project management. It involves a structured approach that aims to determine what the project will deliver, what it will look like, who will be working on it, the time and cost involved, as well as any potential obstacles. This is where ideas are formulated, decisions are made, and the roadmap of the entire development cycle is developed.
Planning has a completely different meaning in software development because software is not a physical product with a fixed shape. Instead, it is built from features, logic, data structures, user experiences, and user behaviors—all of which evolve throughout the development cycle. Unclear requirements can lead to incorrect workflows, and unpredictable timelines can disrupt delivery schedules. This is why project planning in software project management becomes the foundation of every phase that follows. It ensures clarity, aligns teams, reduces risks, and sets a strong roadmap so the final product is delivered with accuracy and efficiency.
Planning also acts as a bridge between the client and development team. Developers are able to bring their technical knowledge and expertise, while clients bring their business challenges, ideas, and expectations. Both sides can move in opposite directions without structured planning. This leads to confusion, rework and frustration. Future-ready planning avoids these problems by creating a vision that guides all parties towards the same result.
In software project management, project planning is a structured process that defines a project's objectives, tasks, timeliness, roles and responsibilities, resources, budgets, risks, technologies and expected outcomes. It provides a roadmap that allows developers, testers and designers to work together in a predictable and coordinated manner.
From idea to deployment, planning is the blueprint.
Future-ready refers to preparing for not only what the project requires today, but also what may evolve in the future. Software is unique because it can continue to evolve even after its initial release through updates, improvements, and new releases. A system today needs to adapt to new features and users, as well as new devices, regulations, and market expectations. The traditional planning approach, which focuses only on the initial delivery, is not able to support this level.
Future-ready planning focuses on flexibility, adaptability, and intelligent forecasting. In modern project planning in software project management, project managers are expected to think beyond deliverables and deadlines. Instead of simply completing tasks, they must anticipate future risks, prepare for upcoming integrations, and ensure the project can scale as technology evolves. With this proactive mindset, teams can build software that remains reliable, efficient, and competitive over the long term.
It is important to note that modern development cycles are heavily dependent on agile frameworks and DevOps, cloud services, APIs from third parties, and digital collaboration in real time. Global teams are working in different time zones and locations, so planning must include digital tools, synchronized workflows and predictive analytics. Future-ready planning does not only mean creating a schedule, but also establishing a robust and resilient development eco-system.
The traditional project plan focused on tasks and deadlines. But modern projects demand:
Future-ready planning is centered on:
Software requirements can change. Flexible scope changes must be allowed in the planning.
Time is saved by using AI-powered tools to estimate, schedule, and report.
Cloud-based tools such as Jira, Trello Asana and ClickUp are ideal for instant collaboration.
Plans must include CI/CD pipelines and automation testing.
Future-ready planning is based on the ability to predict failures and prevent them from happening.
This new approach ensures that the development process is simplified and faster.
The idea is the beginning of every software project, but an idea alone is never enough to build a successful solution. In project planning in software project management, the first and most crucial step is to explore and analyze every requirement in depth. This stage goes far beyond simply understanding what the customer says they want. It requires uncovering why the client needs the solution, how the system should behave, who will use it, what problems it aims to solve, and how it should evolve in the future. This deep exploration ensures clarity, prevents misunderstandings, and lays a strong foundation for a well-planned and result-driven software project.
Project managers will conduct workshops, discussions, meetings, interviews and other activities to gather requirements. They ask detailed, specific questions, they clarify expectations, they understand the complexity of workflows, and then identify any hidden challenges. This process includes analyzing the behavior of the end-user, studying similar systems on the market, and understanding what business objectives software should achieve.
In a future ready environment, requirement discovery becomes more intelligent with the use of prototyping, user journey mapping and cloud-based documentation. This allows clients and development teams early visualization. It reduces the uncertainty of development and aligns all parties before it begins. With well-understood project requirements, you are already half way to success.

Adopting future-ready planning provides significant advantages:
Modern planning helps projects to succeed, even as they become more complex.
The next step after understanding the requirements is to define the scope. Scope is a description of what will be included in the software, what will not be included, and what work will need to be done. Clarity in the scope prevents confusion, especially when there are new ideas or additional features suggested.
Future-ready planning does not just focus on the current features, but also considers future expansions. The planning process should design the system to be modular and scalable, as clients may later want additional features. Software architecture, database structures, and integration abilities should be able to support growth over the long term. It ensures that new updates can be introduced without having to rewrite existing code.
It is only after a clear scope has been defined that schedules, budgets, and tasks can be determined. Without clarity on what needs to be achieved, project planning in software project management becomes nearly impossible. A well-defined scope acts as the foundation for accurate timelines, resource allocation, risk assessment, and overall project execution.
Even after planning, challenges occur. Understanding future-ready planning can help you overcome them.
Solution: Use agile and keep scope flexible
Solution: Break down tasks into smaller sprints.
Solution: Centralize communication using tools
Solution: Documentation and detailed architecture.
Solution: Increase buffer costs and monitor financial performance continuously.
A project road map is an important planning output. The roadmap provides a birds-eye view of your entire development journey. The roadmap breaks down the project into phases, such as analysis and design, development, test, deployment, maintenance, etc. Each phase is broken down further into milestones which define what needs to be done at each stage.
Modern software development does not rely on static or rigid roadmaps. Instead, plans evolve continuously as the project progresses and new insights emerge. In fact, project planning in software project management has shifted toward a more adaptive and flexible approach. Agile and hybrid teams frequently update their roadmaps based on stakeholder feedback, market shifts, and changing priorities. This dynamic planning ensures that the project stays aligned with real business needs rather than outdated assumptions.
Future-ready roadmaps integrate DevOps pipelines, continuous integration environments, automated testing environments and cloud infrastructure. These elements allow for faster deployment cycles.
Make your planning future-proof and advanced:
Future-ready planning is flexible, smart and technology-driven.
The right technology stack is one of the most important decisions to make during software project management. The technology stack includes programming languages, frameworks and databases. It also includes hosting environments, tools, APIs and other technologies. These choices will impact development speed, performance, security and scalability.
Strategic technology selection is required for future-ready planning. The team must determine if the technology is going to be relevant in the future, whether it can be scaled easily, and if developers with the necessary skills are available as part of effective project planning in software project management. Modern projects often depend on cloud platforms and microservices architectures, AI-powered features and automation tools. To avoid future problems, it is important to carefully evaluate all options during the planning phase.
A timeline provides structure and discipline for the development process. It defines the length of each task, milestones to be reached, and dependencies between tasks. Timelines were rigid and fixed in traditional projects. Modern software development demands flexible, realistic and calculated timeframes.
To create future-ready timelines, data from previous projects is used, as well as complexity analysis, risk assessment, and workload forecasting. Project managers can use intelligent tools to automatically adjust timelines in response to delays, progress or changing requirements. It ensures that the developers aren't overloaded, and that deadlines can be met.
The team that works on a software project will determine its success. Resource planning is a process that identifies who will work on what part of the project and which tools they will need. It also identifies how their time will be managed. Teams include architects, designers, developers and testers. They may also include project managers, DevOps Engineers, quality analysts, and DevOps Engineers. Planning ensures that each person has a specific role and responsibilities.
Resource planning that is future-ready pays attention to specializations, workload balances, collaboration, productivity, and skill development. It makes sure that tasks are allocated based on ability, not just availability — a core principle of project planning in software project management. It also prepares backup plans for situations where a teammate becomes unavailable.
Risks are inherent in every project. Risks can include requirements changes, time delays, bugs, budget issues, or security concerns. Future-ready planning identifies risks and develops strategies for addressing them early.
Analytics tools are able to predict delays, identify bottlenecks and estimate workload pressures. This allows teams to respond proactively, rather than reactively.
Documentation is a permanent record. The documentation includes the requirements, scope descriptions and architecture diagrams, as well workflow descriptions, test protocols, and deployment instructions. Without proper documentation, future developers will have a difficult time understanding a system.
Documentation that is future-ready resides on cloud platforms. The team can easily update and access the documentation from anywhere. In project planning in software project management, this approach ensures transparency, clarity, and continuity across all teams.
There are many parties involved in modern software development: clients, designers and developers, testers and managers, and sometimes external vendors. Communication planning ensures that information is easily shared between all parties. The plan will outline how meetings will occur, what tools will be used, and the flow of feedback, helping teams like those at Pmap Technotech Pvt. Ltd. maintain smooth coordination throughout the project.
Future-ready communication is digital, real-time and structured. It reduces confusion, strengthens project planning in software project management, and accelerates the decision-making process.
As technology changes, project planning for software management must adapt. Future-ready planning is not just about creating tasks and deadlines. It is about creating an environment that supports innovation, flexibility and speed, as well as long-term success. It ensures that software projects run smoothly, are aligned with business goals, and offer exceptional value to users.
A project's success is not due to luck, but rather to a well-planned plan. This is the key to a successful project in today's world.
Answer: In software project management, project planning is a structured method of defining all the important elements required to successfully execute a project. It includes gathering requirements, creating timelines and estimating resources. It is the foundation for developers, designers and testers to follow throughout the entire development lifecycle.
Answer: Software development moves so fast that it is important to plan for the future. Technology changes rapidly, user expectations change, and integrations get more complex. A future-ready approach to planning helps teams stay flexible and develop solutions that are scalable and adaptable over time. This ensures that the software remains relevant for a long time after its release.
Answer: To streamline project planning and execution, modern teams use digital collaborative tools. Platforms such as Jira and ClickUp, Asana and Trello, Monday.com and Figma, Confluence and Figma, support everything from design collaboration to code versioning. These tools allow teams to maintain clarity, track their progress and work efficiently.
Answer: The process of planning begins by gathering requirements, which helps to clarify the project's vision. The next step is to define the scope, prepare the schedule, allocate resources and assess potential risks. Planning documentation and communication ensures that the team is aligned throughout the project.
Answer: Agile, Scrum and DevOps methodologies, as well as Hybrid models, play an important role in project planning for the future. These methods focus on continuous improvements, iterative developments, faster delivery, and better collaboration. These approaches offer flexibility, allowing teams to adapt to changing project requirements.
Answer: Planning is essential for reducing uncertainty and risk. It allows teams to anticipate delays, allocate resources judiciously, and maintain realistic deadlines. Planning minimizes rework and improves communication. It also ensures that the project proceeds smoothly.
Answer: Communication is the key element in a project's success. Communication is key to ensuring that stakeholders, clients, and team members are all on the same page about expectations, changes, and progress. Communication that is transparent and structured reduces misunderstandings, speeds up decision-making, and makes the project easier to manage.
Answer: Agile development helps to plan for the future by breaking down the project into manageable, small sprints. Agile development allows for continuous feedback, rapid adjustments and incremental improvements, rather than waiting until the final product is delivered. This flexibility allows teams to respond to changing needs without disrupting their entire plan.
Answer: The documentation is the long-term memory for a software project. It keeps the architecture, requirements and workflows of a system. Documentation makes it easier to maintain consistency and understand the project structure when new team members are added or updates are required.
Answer: To improve their planning, teams can adopt automation, adopt Agile practices, improve communication, maintain updated documentation and use predictive analytics to anticipate risks. Teams can refine their planning strategy over time by incorporating continuous learning, regular reviews and feedback loops.